Alopecia in detail: origins, types, treatment
Partager
I have had alopecia for over 10 years, hence my ongoing research to try to limit its progression through natural products. Here is more information to understand this disease.
Alopecia, more commonly known as hair loss, affects both men and women, regardless of age. This condition results from a complex interconnection between genetic, hormonal, environmental and immune factors. Understanding the origin of alopecia Alopecia, the different variations and possible treatments is essential to understand its impact on self-esteem and explore possible solutions.
The Roots of Alopecia
Alopecia is caused by a variety of factors. Heredity plays a crucial role, with a family history of hair loss increasing the likelihood of being affected. Hormonal fluctuations, whether they occur during pregnancy, menopause or thyroid disorders, also have a significant influence. At the same time, environmental factors such as stress, poor diet and aggressive hairdressing practices can make the condition worse.
The Various Forms of Alopecia
There are different types of alopecia, each with its own characteristics:
-
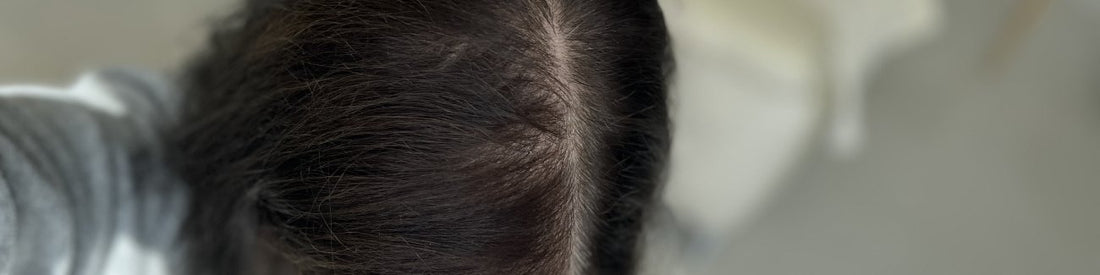
Androgenetic alopecia: Also known as pattern baldness, this variant is the most common form of hair loss. Genetics and hormonal factors interact to primarily influence areas of the scalp in both sexes. Women will lose more hair around their parting, while men will lose more hair on the sides of the forehead and at the top of the head.
-
Alopecia areata: This variety results in hair loss in the form of distinct circular patches. Identified as an autoimmune condition, it results from the immune system attacking the hair follicles.
-
Alopecia totalis/universalis: This rare form causes the loss of all hair on the scalp or even the entire body, including body hair.
-
Cicatricial alopecia: Causing skin scars, burns or infections, this variant causes the irreversible destruction of hair follicles.
Standard solutions for treating alopecia
The choice of treatment depends on the type and severity of hair loss. Options include:
-
Drug Treatments: Minoxidil and finasteride, among others, may be prescribed to stimulate hair growth and slow hair loss.
-
Corticosteroid therapies: Used for variant areata, they suppress the local immune response.
-
Light therapy: Laser treatment can promote hair regrowth by improving blood circulation to hair follicles.
-
Hair Transplant Surgery: In cases of advanced hair loss, hair transplantation involves transferring healthy follicles to the bald areas.
-
Hair care and natural products: A balanced diet, stress management, gentle hairdressing practices and vegetable oils.
This is the last point that I have been applying for years, after stopping my chemical treatment with minoxidil to use only natural products. You will find on this site my advice, products and recipes to successfully limit your hair loss naturally.
If this disease is recent for you and is developing rapidly, I strongly advise you to go see a hair specialist to make a diagnosis and help you define the best solution for you. This disease differs from person to person and my advice will not necessarily be enough to improve aggravated stages of the disease.













